Serialization with Dataclasses Avro Schema
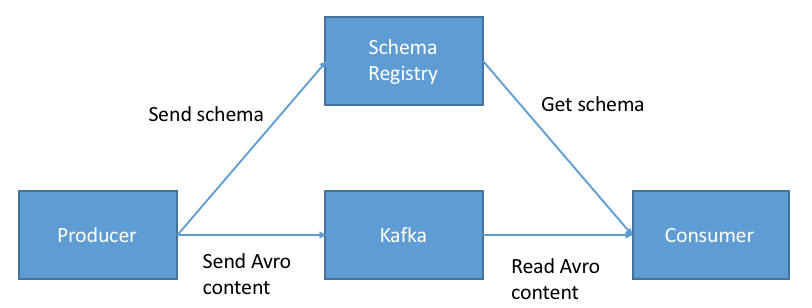
Last year I released the project Dataclasses Avro Schema in wich the main goal was to generate avro schemas from python dataclass. Thanks to this main feature, is possible to serialize/deserialize python instances using the self contain avro schemas. For example, we can serialize python instances in order to create events and place them (binary) in kafka topics or redis streams and also we can deserialize the events and convert them into the original python instances. This is a powerful feature, because the data layer for streaming application is full covered with this library, meaning that you can use your favorite python kafka driver or python redis driver to built streaming application without worries of the data model.
Serialization
Serialization can be done using avro, avro-json or json on a python instance:
from dataclasses import dataclass import typing from dataclasses_avroschema import AvroModel @dataclass class Address(AvroModel): "An Address" street: str street_number: int address_data = { "street": "test", "street_number": 10, } # create an Address instance address = Address(**address_data) address.serialize() # >>> b'\x08test\x14' address.serialize(serialization_type="avro-json") # >>> b'{"street": "test", "street_number": 10}' # Get the json from the instance address.to_json() # python dict >>> {'street': 'test', 'street_number': 10}
Deserialization
Deserialization can be done as well with avro or avro-json. You must know beforehand which one you should use
avro_binary = b'\x08test\x14' # Address instance serialized with avro Address.deserialize(avro_binary) # create a python instance of Address # >>>> Address(street='test', street_number=10) avro_json = b'{"street": "test", "street_number": 10}' # Address instance serialized with avro-json Address.deserialize(avro_json, serialization_type="avro-json") # create a python instance of Address # >>>> Address(street='test', street_number=10)
Examples with kafka and redis drivers
You can create simple straming applications using your favorite python driver either kafka or redis and integrate producers and consumers with dataclasses-avroschema. The following is a minimal example using aiokafka:
import asyncio from dataclasses import dataclass import random from aiokafka import AIOKafkaConsumer, AIOKafkaProducer from dataclasses_avroschema import AvroModel, types @dataclass class UserModel(AvroModel): "An User" name: str age: int favorite_colors: types.Enum = types.Enum(["BLUE", "YELLOW", "GREEN"], default="BLUE") country: str = "Argentina" address: str = None class Meta: namespace = "User.v1" aliases = ["user-v1", "super user"] async def consume(loop, total_events=10): consumer = AIOKafkaConsumer( 'my_topic', 'my_other_topic', loop=loop, bootstrap_servers='localhost:9092', group_id="my-group") # Get cluster layout and join group `my-group` await consumer.start() run_consumer = True while run_consumer: try: # Consume messages async for msg in consumer: print(f"Message received: {msg.value} at {msg.timestamp}") user = UserModel.deserialize(msg.value) print(f"Message deserialized: {user}") except KeyboardInterrupt: # Will leave consumer group; perform autocommit if enabled. await consumer.stop() print("Stoping consumer...") run_consumer = False async def send(loop, total_events=10): producer = AIOKafkaProducer( loop=loop, bootstrap_servers='localhost:9092') # Get cluster layout and initial topic/partition leadership information await producer.start() for event_number in range(1, total_events + 1): # Produce message print(f"Sending event number {event_number}") user = UserModel( name=random.choice(["Juan", "Peter", "Michael", "Moby", "Kim",]), age=random.randint(1, 50) ) # create the message message = user.serialize() await producer.send_and_wait("my_topic", message) # sleep for 2 seconds await asyncio.sleep(2) else: # Wait for all pending messages to be delivered or expire. await producer.stop() print("Stoping producer...") if __name__ == "__main__": loop = asyncio.get_event_loop() tasks = asyncio.gather(send(loop), consume(loop)) loop.run_until_complete(tasks)
Under examples folder you can other two kafka examples (sync) using the kafka-python driver, where the avro-json serialization and schema evolution (FULL compatibility) is shown.
Also, there are two redis examples using redis streams with walrus and redisgears-py
Factory and fixtures
Dataclasses Avro Schema also includes a factory feature, so you can generate fast python instances and use them, for example, to test your data streaming pipelines. Instances can be genrated using the fake method.
import typing from dataclasses_avroschema import AvroModel class Address(AvroModel): "An Address" street: str street_number: int class User(AvroModel): "User with multiple Address" name: str age: int addresses: typing.List[Address] Address.fake() # >>>> Address(street='PxZJILDRgbXyhWrrPWxQ', street_number=2067) User.fake() # >>>> User(name='VGSBbOGfSGjkMDnefHIZ', age=8974, addresses=[Address(street='vNpPYgesiHUwwzGcmMiS', street_number=4790)])
Conclusion
If you are starting a straming python application, give it a try to Dataclasses Avro Schema in order to cover the data model layer, and avoid headaches at the moment of serializarion/deserialization process.